Did Judge Juan M. Merchan tell jurors in the Donald Trump hush-money trial that they didn't have to reach a unanimous verdict? No, that's not true: The transcript of his instructions to the jury shows that Merchan said, "Your verdict, on each count you consider, whether guilty or not guilty, must be unanimous." Two law school faculty members rejected the claim that the judge ever told the jury otherwise.
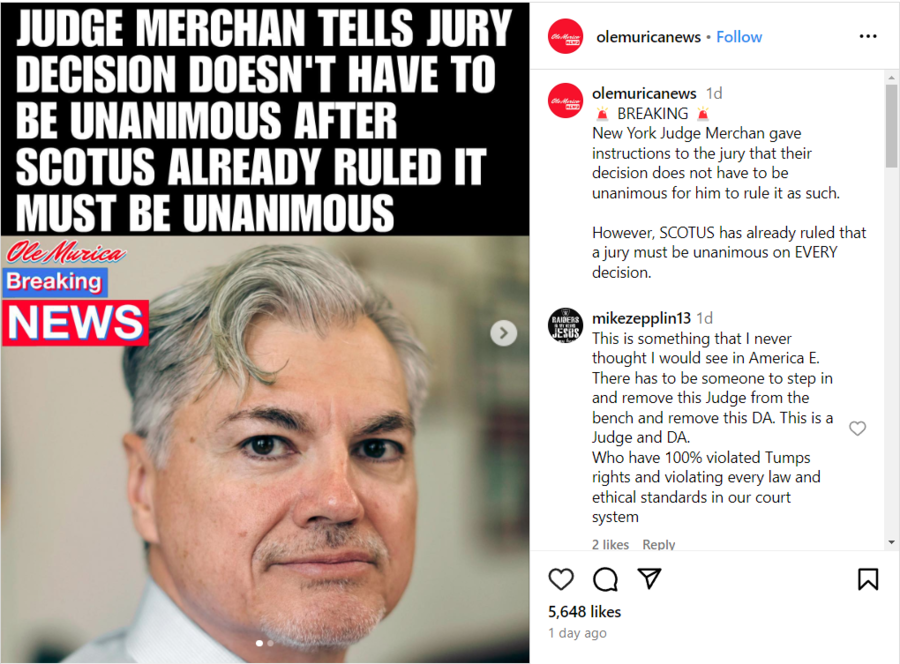
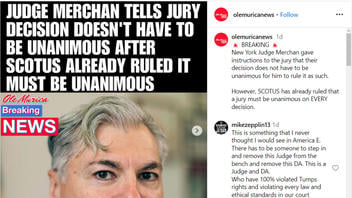
The claim appeared in a post (archived here) on Instagram by olemuricanews on May 29, 2024, under the on-screen title "JUDGE MERCHAN TELLS JURY DECISION DOESN'T HAVE TO BE UNANIMOUS AFTER SCOTUS ALREADY RULED IT MUST BE UNANIMOUS." The post's caption said:
🚨 BREAKING 🚨
New York Judge Merchan gave instructions to the jury that their decision does not have to be unanimous for him to rule it as such.
However, SCOTUS has already ruled that a jury must be unanimous on EVERY decision.
This is what the post looked like on Instagram at the time of writing:
(Source: Instagram screenshot taken on Fri May 24 17:15:32 2024 UTC)
The post provided no attribution or other evidence to substantiate the claim.
Jury instructions
In his lengthy instructions to the jury (archived here) on May 29, 2024, Merchan clearly stated that the jury must reach a unanimous decision on each of the 34 counts against the former president (emphasis ours):
Your verdict, on each count you consider, whether guilty or not guilty, must be unanimous. In order to find the defendant quilty, however, you need not be unanimous on whether the defendant committed the crime personally, or by acting in concert with another, or both.
The right to a unanimous jury in a criminal case is guaranteed under the Sixth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution and was confirmed for criminal cases at the state level in 2020 by the U.S. Supreme Court in Ramos v. Louisiana.
Legal experts
Lori Hoetger, an assistant professor at the University of Nebraska College of Law, called the social media post "misleading if not downright inaccurate." In a May 31, 2024, email to Lead Stories, she said:
The law requires the jury's vote on guilty or not guilty to be unanimous - in other words, all 12 jurors had to all vote guilty for the jury to return a vote of guilty.
The reason for the confusion, though, is because the State charged 34 counts of Falsifying Business Records in the First Degree, which required the State to prove beyond a reasonable doubt that the defendant intended to defraud that includes an intent to commit (or aid/conceal) another crime (emphasis my own).
So part of the jury's finding of guilt required each juror to agree that the defendant had an intent to defraud in committing some other crime.
Hoetger continued:
But--and here is where it gets confusing--the jury did not have to be unanimous on what that other crime is.
So the State could present evidence of several different possible crimes (e.g., election law violation, tax fraud) as alternate theories of what crime the defendant intended to commit.
Each member of the jury would have to agree that the defendant intended to commit at least one of these crimes, but they did not have to be unanimous on which crime they believe the State proved beyond a reasonable doubt.
In a May 31, 2024, phone interview with Lead Stories, Kay Levine, an associate dean and professor at Emory University School of Law in Atlanta, echoed Hoetger's analysis of the judge's jury instructions. She said:
Juries, of course, have to reach a unanimous verdict. They have to agree that the prosecution has proven guilt for each element of the crime beyond a reasonable doubt.
What they don't have to agree on here is what the underlying offense was. That is the particular fraud that was being advanced by the defendant's behavior in falsifying the business records.
Later in the interview, Levine restated her explanation. She said:
They [members of the jury] have to agree that representatives of the Manhattan DA's office proved beyond a reasonable doubt the elements of the various crimes of falsifying business records, but they don't have to have agreed on which type of fraud was intended to be accomplished by falsifying those business records.
Read more
Other fact check agencies have also reviewed this claim, including the Associated Press, USA Today and AFP.
Additional Lead Stories fact checks about Judge Merchan can be found here and about Donald Trump can be found here.