Is there "still no evidence masks or lockdowns slow the spread of COVID-19"? No, that's not true: The claim was posted with no citation of studies disproving the effectiveness of masks and lockdowns. On the other hand, there are now dozens of scientific studies published showing that wearing masks and instituting lockdowns or stay-at-home orders have been effective in slowing the spread of the virus that causes COVID-19.
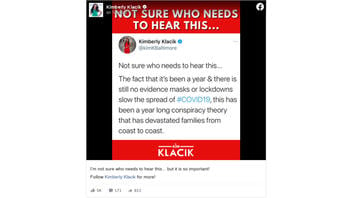
The claim appeared in a Facebook post (archived here) where it was published February 23, 2021 under the title "I'm not sure who needs to hear this... but it is so important! "It opened:
Not sure who needs to hear this...
The fact that it's been a year & there is
still no evidence masks or lockdowns
slow the spread of #COVID19, this has
been a year long conspiracy theory
that had devastated families from
coast to coast
This is what the post looked like on Facebook at the time of writing:
(Source: Facebook screenshot taken on Thu Feb 25 08:45:13 2021 UTC)
A review of face mask studies and related scientific literature published January 26, 2021 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal found that the "literature offers evidence in favor of widespread mask use as source control to reduce community transmission."
A study published June 3, 2020 in the Applied Health Economics and Health Policy journal found that lockdown policies "have been able to reduce the number of COVID-19 cases in the countries that implemented them."
A year into the pandemic, evidence has accumulated showing how face masks work in slowing the transmission of COVID-19 infection. For example, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention refers to some of the research in a section on its website discussing the effectiveness of cloth masks in controlling the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Lead Stories has done several fact checks that point to the scientific research in debunking claims that masks do not effectively control the spread of the virus.
The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal article cites more than 140 articles, including studies and scholarly papers, regarding the effectiveness of masks:
The science around the use of masks by the public to impede COVID-19 transmission is advancing rapidly. In this narrative review, we develop an analytical framework to examine mask usage, synthesizing the relevant literature to inform multiple areas: population impact, transmission characteristics, source control, wearer protection, sociological considerations, and implementation considerations.
A primary route of transmission of COVID-19 is via respiratory particles, and it is known to be transmissible from presymptomatic, paucisymptomatic, and asymptomatic individuals. Reducing disease spread requires two things: limiting contacts of infected individuals via physical distancing and other measures and reducing the transmission probability per contact. The preponderance of evidence indicates that mask wearing reduces transmissibility per contact by reducing transmission of infected respiratory particles in both laboratory and clinical contexts. Public mask wearing is most effective at reducing spread of the virus when compliance is high.
The Facebook claim also says that lockdown policies are ineffective. Lockdown policies in the United States were more common during the winter and spring of 2020 when COVID-19 infections first started escalating. Many of the studies evaluating the effectiveness of lockdowns in the U.S. and Europe look at that time period, including the study published in the Applied Health Economics and Health Policy journal look at that time period. The study found:
Our results show that lockdown is effective in reducing the number of new cases in the countries that implement it, compared with those countries that do not. This is especially true around 10 days after the implementation of the policy. Its efficacy continues to grow up to 20 days after implementation.